Only mathematics and mathematical logic can say as little as the physicist means to say.
The routines.
AndIsFalse()
AndIsFalse(Expressions)
-
Expressions, array, an array of Boolean expressions.
AndIsFalse() takes an array of Boolean expressions like in the example below. If all are indeed false, it returns true, if one or more are true, the result is false.
echo(AndIsFalse([2 > 4, 5 < 0, "ed" == "ted"]));
echo(AndIsFalse([2 > 4, 5 < 0, "ed" == "ed"]));
ECHO: true
ECHO: falseAndIsTrue()
AndIsTrue(Expressions)
-
Expressions, array, an array of Boolean expressions.
AndIsTrue() takes an array of Boolean expressions like in the example below. If all are indeed true, it returns true, if one or more are false, the result is false.
echo(AndIsTrue([2 < 4, 5 > 0, "ed" == "ed"]));
echo(AndIsTrue([2 < 4, 5 > 0, "ed" == "ted"]));
ECHO: true
ECHO: falseATan2()
ATan2(X,Y)
-
X, Y, coordinates.
Unlike the native atan2(), which takes the coordinates in reverse order (please do
explain this to me) and returns values [-180…180], ATan2() expects its parameters in a logical order, and returns values [0…360], which may seem more logical, and is possibly more convenient. Is it essential? No. Indispensable? Probably not. Requisite, then, at least? Perhaps…
function ATan2(X,Y)=
(atan2(Y,X)+360)%360
;
echo(ATan2(-2,-2));
ECHO: 225
BinomialCoefficient()
BinomialCoefficient(N,K)
-
N, integer, binomial power (1 + x)n (and row in Pascal’s triangle)
-
K, integer, the xk term in the expansion (and element in the row)
BinomialCoefficient(N,K) is the coefficient of the xk term in the polynomial expansion of the binomial power (1 + x)n.
If that’s clear as mud because math wasn’t your favourite subject, don’t worry about it. You’ll never need it; it’s only here because
GBezierPoint() uses it, and if anything happens anywhere in The GHOUL, I aim to document it. Really, I mean it, don’t worry.
Clip()
Clip(Value,Min,Max)
-
Value, value to be 'clipped'.
-
Min, lower clipping limit.
-
Max, upper clipping limit.
Clip() allows you to write Baz=Clip(Foo,0,10) instead of Baz=min(max(Foo,0),10). It’s a little trivial, I know, but I like the looks better and the code reads easier, in my opinion, and, here, I am King.
Foo=12;
Baz=Clip(Foo,0,10);
echo(Baz);
ECHO: 10ColorHexToTuple()
ColorHexToTuple(HexColor)
-
HexColor, OpenSCAD hexadecimal color notation, e.g., #FF8000.
Convert an OpenSCAD hexadecimal color notation into an OpenSCAD color-tuple. Used by Intermediate().
echo(ColorHexToTuple("#FF8000");
ECHO: [1,0.5,0]ColorTupleToHex()
ColorTupleToHex(ColorTuple)
-
ColorTuple, OpenSCAD color tuple, e.g., [1,0.5,0].
Convert an OpenSCAD color-tuple into an OpenSCAD hexadecimal color notation. Used by Intermediate().
echo(ColorTupleToHex([1,0.5,0]);
ECHO: "#FF8000"DayOfTheWeek()
DayOfTheWeek(Year,Month,Day)
-
Year, Month, Day, integers, like 1969, 7, 21, in that order, because 'Day, Month, Year' would only confuse the people living between Canada and the United Mexican States.
Only valid for years after 1752 (in the U.K.). Returns 0 for Sunday, 1 for Monday and so on. WeekDays is set in Definitions/Constants.scad, so you can use WeekDays[DayOfTheWeek(Year,Month,Day)] for string output.
echo(WeekDays[DayOfTheWeek(1969,7,21)]); // And what a day it was...
ECHO: "Monday"Decimals()
Decimals(Value,Decimals)
-
Value, scalar.
-
Decimals, integer, maximum number of decimals to remain.
Crops Value to a length of maximal Decimals decimals.
echo(Decimals(1.2345,2));
ECHO: 1.23DecToHex()
DecToHex(Dec)
-
Dec, integer.
DecToHex() does what it says on the tin. Non-integers are floor()-ed.
Deg()
Deg(Radians)
-
Radians, radians to be converted.
Deg() allows you to write Baz=Deg(3.63) instead of Baz=3.63/Tau*360. It’s also a bit trivial, I know, but it definitely makes for prettier code.
Foo=3.63;
Baz=Deg(Foo);
echo(Baz);
ECHO: 207.984Factorial()
Factorial(Int)
-
Int, integer to calculate the factorial of.
Factorial(), unsurprisingly, calculates the factorial.
echo(Factorial(5));
ECHO: 120GreatestCommonDivisor()
GreatestCommonDivisor(Value1,Value2)
-
Value1,Value2, integers to calculate the greatest common divisor of, or give Value1 an array of integers and leave Value2 undef.
GreatestCommonDivisor(), calculates the greatest common divisor of two integers or an array of integers. It does this by replacing the higher value with the modulo of the two until that reaches 0, the remaining value is then the GCD. GreatestCommondDivisor() is the contender for the longest function name in The GHOUL, the current holder of the title is SearchPrintableCharacters(), like I already said somewhere else: there is a limit.
|
|
If you’d rather not have 21-letter function names in your code, there’s GCD(); a shorter-but-not-so-descriptive alias for GreatestCommondDivisor()
|
echo(GreatestCommonDivisor(12,31));
/*
The iterations are:
31-12
12-7
7-5
5-2
2-1
1-0
*/
ECHO: 1HexToDec()
HexToDec(Hex)
-
Hex, string, initial "#" is scrubbed, uses HexCharLow, so upper and lowercase are accepted.
HexToDec() does what it says on the tin. Hex strings with or without a leading # are accepted, as are upper- and lower case characters or a mixture of both.
echo(HexToDec("#FD3e"));
ECHO: 64830InchFraction()
InchFraction(Value,Res=16)
-
Value, scalar.
-
Res, resolution, smallest allowable division in which to express Value, one of [2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64], defaults to 16 for one 1/16th of an Inch.
Returns Value as a string, formatted to the familiar divisions used for inches, reduced as far as possible, but forced to a resolution of no more than Res.
echo(InchFraction(0.375));
echo(InchFraction(0.375,2));
echo(InchFraction(4.625,32));
ECHO: "0-3/8"
ECHO: "0-1/2"
ECHO: "4-5/8"InlineVertex()
InlineVertex(Vertex1,Vertex2,Coordinate)
-
Vertex1, Vertex2, 3D vertices.
-
Coordinate, coordinate, only one of the X,Y or Z coordinates may be given, as a scalar, the remaining coordinates must be undef, like [undef,1,undef].
InlineVertex() returns a vertex that is situated on the line through Vertex1 and Vertex2, on a plane normal to one of the axis, of which only one coordinate is known, e.g., [undef,0,undef]. In the example the plane is Y=0, but any plane not parallel to the line will yield results.
P1=[0,10,0];
P2=[0,5,3];
Coord=[undef,0,undef];
echo(InlineVertex(P1,P2,Coord));
ECHO: [0,0,6]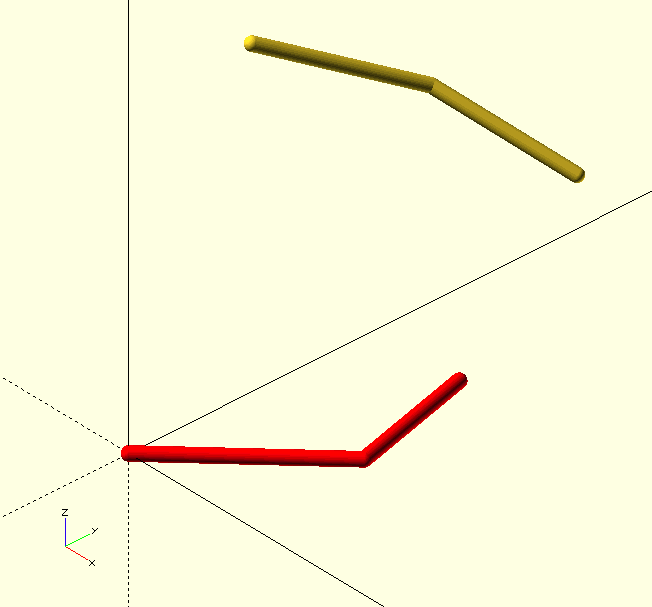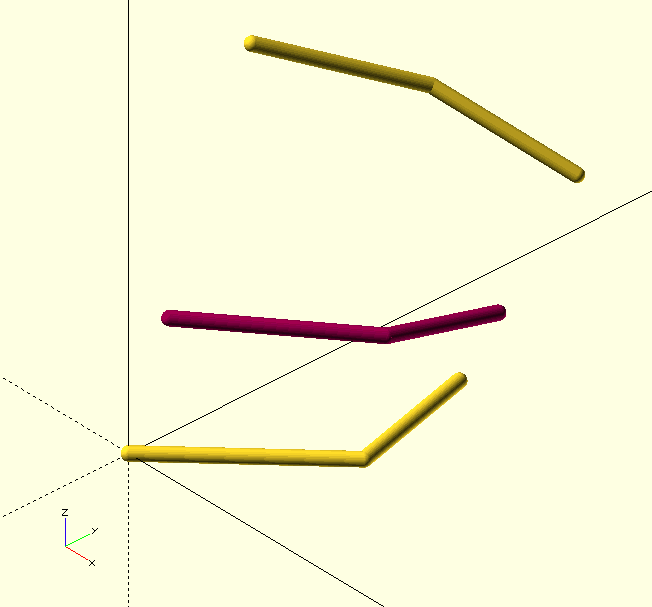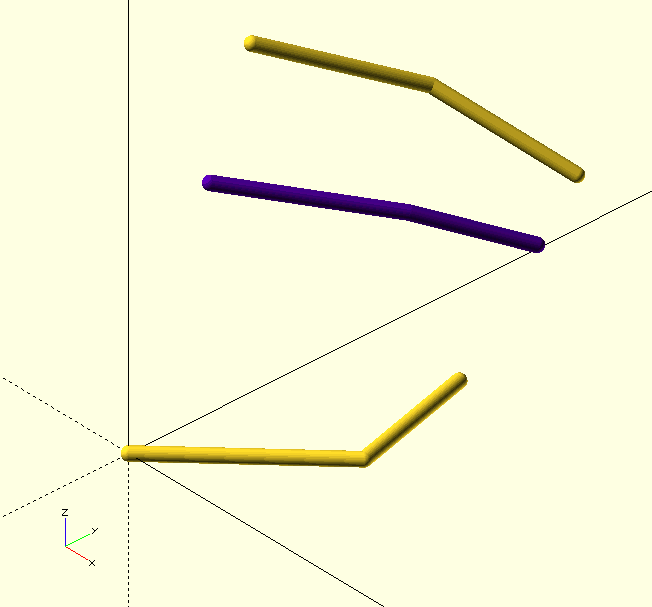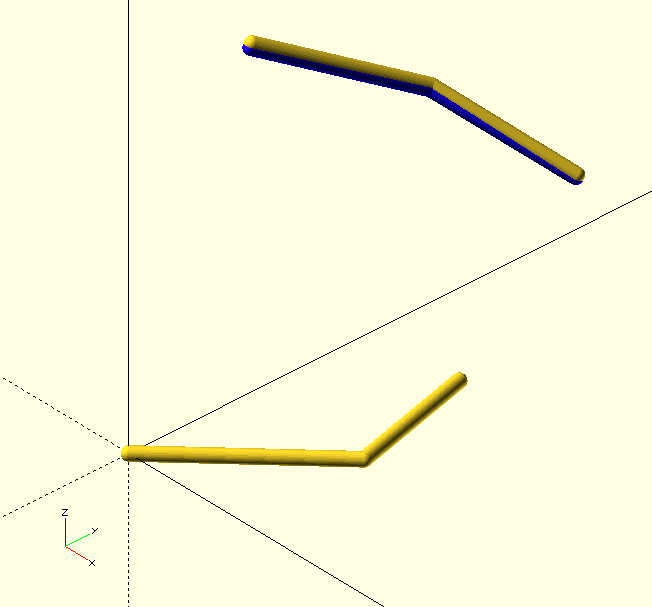
Intermediate()
Intermediate(Start,End,Frac)
-
Start, value, tuple or array.
-
End, value, tuple or array.
-
Frac, a fraction 0=<Frac=<1 (although 0 and 1 wouldn’t make much sense).
Intermediate() returns the intermediate value, tuple or array between Start and End at Frac of the difference from Start. It can be used for an intermediate curve, point, or even a color definition (including The GHOUL’s predefined Hex colors) or a single value. It is clever enough to return values in the correct type.
echo(Intermediate([[0,0],[10,10]],[[5,10],[30,20]],0.4));
echo(Intermediate([10,10],[30,20],0.4));
echo(Intermediate([10],[20],0.4));
echo(Intermediate(10,20,0.4));
// The GHOUL predefined colors are returned as Hex strings.
echo(Intermediate(RED,BLU,0.4)); // Quite a pretty purple...
ECHO: [[2, 4], [18, 14]]
ECHO: [18, 14]
ECHO: [14]
ECHO: 14
ECHO: "#990066"
/* The code for image above: */
Start=[[0,0,0],[4,4,0],[3,8,0]];
End=[[0,4,10],[2,8,8],[5,10,6]];
ShowCurve(Start,0.2,Connect=true);
ShowCurve(End,0.2,Connect=true);
color(Intermediate(RED,BLU,$t))
ShowCurve(Intermediate(Start,End,$t),0.2,Connect=true);
Interpolate()
Interpolate(Domain,Range,Value)
-
Domain, tuple, value pair of Min and Max input values [Min,Max].
-
Range, tuple, value pair of Min and Max result values [Min,Max].
-
Value, value, on, or outside of Domain.
Interpolate() returns the value from Range, proportionally corresponding to the position of Value on Domain. If Value lies outside of Domain, Interpolate() effectively becomes 'Extrapolate()', which, for that reason, doesn’t exist…
echo(Interpolate([0,10],[80,100],3.2));
echo(Interpolate([0,10],[80,100],-2));
ECHO: 86.4
ECHO: 76Is…()
Is…(I)
-
I, scalar, fraction or integer to be analised.
IsMath.scad contains several functions that test numbers and return either true or false.:
| IsEven(I) |
true if I is an even integer. |
| IsOdd(I) |
true if I is an odd integer. |
| IsInterger(I) |
true if I is an integer. |
| IsNotInterger(I) |
true if I is not an integer. |
| IsFraction(I) |
true if I is a fraction 0<I<1. |
| IsNumber(I) |
true if I is any kind of number. |
| IsPositive(I) |
true if I is a positive number 0<I. |
| IsNegative(I) |
true if I is a negative number I<0. |
LeastCommonMultiple()
LeastCommonMultiple(Value1,Value2)
-
Value1,Value2, integers to calculate the least common multiple of, or give Value1 an array of integers and leave Value2 undef.
echo(LeastCommonMultiple([32,12,56]));
ECHO: 672Map()
Map(Value,Min,Max)
-
Value, scalar to map.
-
Min, scalar, although most likely an integer, lower mapping limit.
-
Max, scalar, although most likely an integer, upper mapping limit, excluded.
Circular map Value onto an interval so that the lower limit Min maps onto itself, and the upper limit Max maps back onto the lower, i.e., map Value onto [Min…Max).
Result=Map(Value,4,8); Value : 3.3 12 13.5 14 15 16 17... Result : 7.3 4 5.5 6 7 4 5...
There is a special version of Map(), specifically for 'circular addressing' an array, have a look at
Dex().
|
|
Map.scad also contains a handful of shortcuts for common Value ranges, such as Map12(), Map24(), Map60(), Map360(), and MapTau(), they all have 0 as the lower limit.
|
MCeil()
MCeil(Value,Factor)
-
Value, scalar, value to be rounded up.
-
Factor, scalar, rounding multiplier.
MCeil() rounds Value up to the nearest multiple of Factor.
echo(MCeil(5.31,0.25));
ECHO: 5.5MFloor()
MFloor(Value,Factor)
-
Value, scalar, value to be rounded down.
-
Factor, scalar, rounding multiplier.
MFloor() rounds Value down to the nearest multiple of Factor.
echo(MCeil(5.31,0.25));
ECHO: 5.25Mod()
Mod(Value,Modulus)
-
Value, scalar, value to be reduced.
-
Modulus, integer, modulus.
Mod() is identical to the native OpenSCAD modulo operator %. It’s just here because, well, I’m bothered that N%0 returns nan to be honest; what was wrong with undef? Oh, well…
|
|
Mod.scad also contains a handful of shortcuts for common Values, such as Mod1(), Mod2(), Mod360(), and ModTau().
|
echo(Mod360(402));
ECHO: 42MostSignificant()
MostSignificant(Value)
-
Value, decimal fraction.
Returns the index of the most significant digit in a fraction when converted to a string.
echo(4/91);
echo(MostSignificant(4/91));
ECHO: 0.043956
ECHO: 3MRound()
MRound(Value,Factor)
-
Value, scalar, value to be rounded.
-
Factor, scalar, rounding multiplier.
MRound() rounds Value to the nearest multiple of Factor.
echo(MRound(5.31,0.25));
ECHO: 5.25NDecimal()
NDecimal(Value,N)
-
Value, scalar, value to be processed.
-
N, integer, decimal index.
NDecimal() returns the decimal at the N position in Value. N is 0-based.
echo(NDecimal(12.1234567,3));
ECHO: 4NearestEven()
NearestEven(Value)
-
Value, scalar.
NearestEven() returns the nearest even integer to Value. It is an alias for MFloor(Value+1,2). When Value is an odd integer, the nearest larger, i.e., more positive, even integer is returned.
echo(NearestEven(31.01));
echo(NearestEven(32.99));
echo(NearestEven(33));
ECHO: 32
ECHO: 32
ECHO: 34NearestOdd()
NearestOdd(Value)
-
Value, scalar.
NearestOdd() returns the nearest odd integer to Value. It is an alias for MFloor(Value,2)+1. When Value is an even integer, the nearest larger, i.e., more positive, odd integer is returned.
echo(NearestOdd(30.01));
echo(NearestOdd(31.99));
echo(NearestOdd(32));
ECHO: 31
ECHO: 31
ECHO: 33OffLimits()
OffLimits(Value,Min,Max,Clip=true)
-
Value, scalar.
-
Min, Max, limits.
-
Clip, Boolean, clip Value, defaults to true.
If Value equals one of the limits, it gets nudged into the specified, acceptable range. If Clip=true, and Value falls outside the limits, it is first clipped to the nearest limit, and then nudged off. Used for avoiding 0 and other values that break subsequent calculations.
The 'nudge' used is Thought (defined in Definitions/Constants.scad), a very small value. Almost nothing, well, not quite nothing; it’s 1/4096 (2^12), so less than a second (You know; degree-minute-second.)
OrderOfMagnitude()
OrderOfMagnitude(Value)
-
Value, scalar.
Returns the order of magnitude of Value. Unsurprisingly. Copes handsomely with scientific notation.
echo(OrderOfMagnitude(0.0001));
echo(OrderOfMagnitude(1000));
echo(OrderOfMagnitude(1/pow(10,12)));
echo(OrderOfMagnitude(1e16));
ECHO: -4
ECHO: 3
ECHO: -12
ECHO: 16OrIsFalse()
OrIsFalse(Expressions)
-
Expressions, array, an array of Boolean expressions.
OrIsFalse() takes an array of Boolean expressions like in the example below. If one is false, it returns true, if none are false, the result is false. It is an alias for !AndIsTrue().
echo(OrIsFalse([2 < 4, 5 > 0, "ed" == "ted"]));
echo(OrIsFalse([2 < 4, 5 > 0, "ed" == "ed"]));
ECHO: true
ECHO: falseOrIsTrue()
OrIsTrue(Expressions)
-
Expressions, array, an array of Boolean expressions.
OrIsTrue() takes an array of Boolean expressions like in the example below. If one is true, it returns true, if none are true, the result is false. It is an alias for !AndIsFalse().
echo(OrIsTrue([2 > 4, 5 < 0, "ed" == "ed"]));
echo(OrIsTrue([2 > 4, 5 < 0, "ed" == "ted"]));
ECHO: true
ECHO: falsepow() Aliases
The GHOUL offers a few pow() aliases to make things just a little easier:
Sqrt(Value) = pow(Value,0.5)
Pow2(Value) = pow(Value,2)
Pow3(Value) = pow(Value,3)
Pow10(Value) = pow(Value,10)
Rad()
Rad(Degrees)
-
Degrees, degrees to be converted.
Rad() allows you to write Baz=Rad(65) instead of Baz=65/360*Tau. It’s also a bit trivial, I know, but it definitely makes for prettier code.
Foo=65;
Baz=Rad(Foo);
echo(Baz);
ECHO: 1.13446Rnd()
Rnd(Seed=undef)
-
Seed, scalar, random seed for repeatable results.
Returns a pseudo random number between 0 and 1. Providing a seed will give repeatable results.
Sequence()
Sequence(Start=0,Step=$fs,End)
-
Start, scalar, start of the sequence.
-
Step, scalar, step size of the sequence.
-
End, scalar, end of the sequence.
Returns an array [Start…End] in segments the size of Step (defaults to $fs). The first and last values in the array are ALWAYS Start and End. Step will be adjusted so that all steps are of one, equal size.
If Step is negative, there will be abs(Step) steps (and thus Steps+1 values).
Sign()
Sign(Value)
-
Value, scalar.
Returns 1 or -1 commensurate with the sign of 'Value'. This returns 1 when Value=0, unlike the native sign(), which returns 0 in this case.
UndefFallback()
UndefFallback(Value,Replacement=true)
-
Value, any type of variable to be processed.
UndefFallback() prevents undef values that may break your functions or modules, by replacing Value only when it is undef, with Replacement, defaults to true.
echo(UndefFallback(undef,[0,90,0]));
ECHO: [0,90,0]ZeroFallback()
ZeroFallback(Value,Replacement=Frogshair)
-
Value, scalar, scalar to be processed.
ZeroFallback() prevents 0 values that may break your functions or modules, by replacing Value only when it is 0, with Replacement, defaults to Frogshair, which is defined in TheGHOUL/Lib/Definitions/Constants.scad as 1/16384.
echo(ZeroFallback(0,5));
ECHO: 5